What is a warehouse? At its core, it’s a space used to store physical goods before they are sold, used, or shipped. It helps businesses organize, protect, and manage their inventory. Warehousing plays a key role in supply chains—especially when customer demand, production, and shipping don’t line up perfectly.
Whether you’re running a small online shop or a global company, if you sell physical products, a warehouse often becomes a must.
Warehousing Definition
Warehousing means storing goods in a dedicated space and managing them until they’re needed. It includes receiving items, keeping track of stock, picking products for orders, and sending them out.
So, it’s more than just storage. It’s an organized process that keeps things moving smoothly.
What Happens in a Warehouse?
Inside a warehouse, the flow of goods follows a system:
- Goods arrive (from suppliers or production)
- They’re checked and logged
- Products are stored safely
- Orders are picked and packed
- Items are shipped to retailers or customers
All of this is tracked, managed, and optimized—often with the help of warehouse management systems (WMS).
Types of Warehouses
Different businesses need different warehouse setups. Here are the main types:
- Private Warehouse: Owned or rented long-term by one company.
- Public Warehouse: Shared storage space rented by the pallet or square meter.
- Co-op Warehouse: Shared by a group of businesses in the same industry.
- Distribution Center: Focuses on quick movement of goods, not long-term storage.
- Climate-Controlled Warehouse: For goods that need temperature or humidity control.
Some businesses also use third-party warehousing, which means outsourcing storage and logistics to a specialized company.
What Are the Different Parts of a Warehouse?
A warehouse isn’t just one big room full of shelves. Even the simplest setup has a few key areas that keep everything running smoothly.
At a basic level, a warehouse usually includes:
- Access doors – for receiving and shipping goods
- Storage area – where inventory is kept
- Open floor space – for maneuvering and checking items
- Management office – for handling operations and paperwork
- Toilets and changing rooms – for staff
As operations grow, other zones get added, such as:
- Reception area – where goods are checked and verified
- Packaging and consolidation – to prepare orders for shipping
- Dispatch area – where goods are sorted and sent out
- Loading docks – for trucks to load and unload
- Battery charging stations – for electric forklifts
Some warehouses go further and divide space based on product type or how often items move. For example:
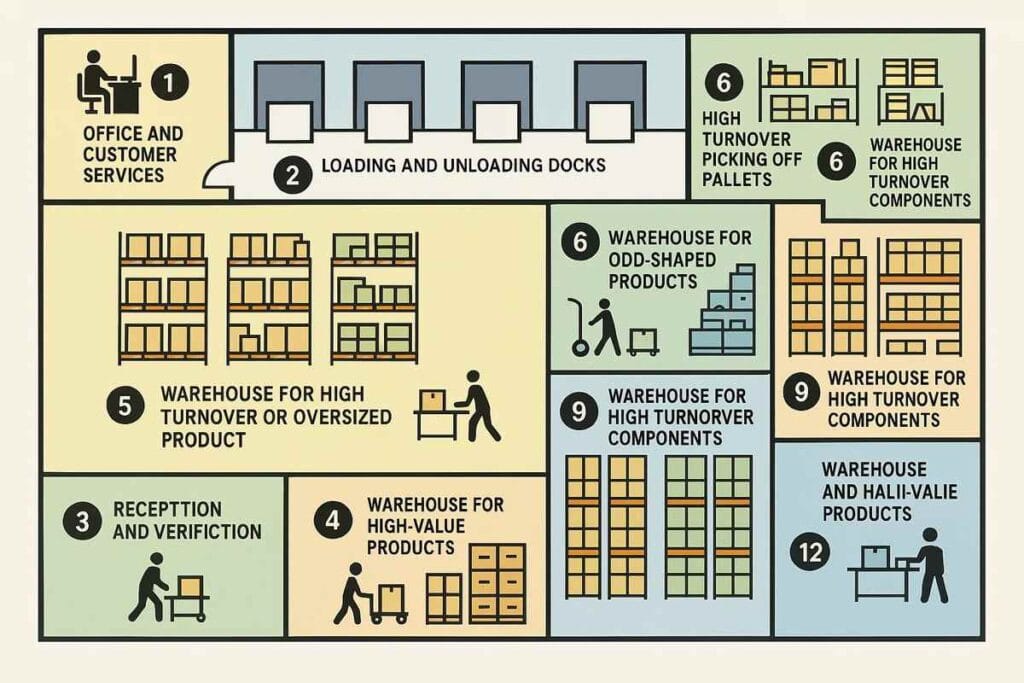
- Office and customer service
- Loading/unloading docks
- Goods reception and inspection
- Outbound dispatch area
- Fast-moving or oversized goods zone
- Pallet picking for high-turnover items
- Section for bulky or odd-shaped products
- Medium-turnover components
- High-turnover components
- Low-turnover components
- Secure storage for high-value items
- Final packaging and order consolidation
Each area plays a specific role in making sure inventory flows efficiently, workers stay safe, and orders are fulfilled on time. How a warehouse is laid out depends on the type of business, product range, and daily activity level.
Third Party Warehousing Definition
A third-party warehouse is a facility operated by a logistics provider, not the business itself. You pay them to store your goods and sometimes even handle packaging, shipping, and returns.
It’s ideal for small businesses, seasonal brands, or anyone who wants flexibility without investing in their own warehouse space.
What Is Warehouse Logistics?
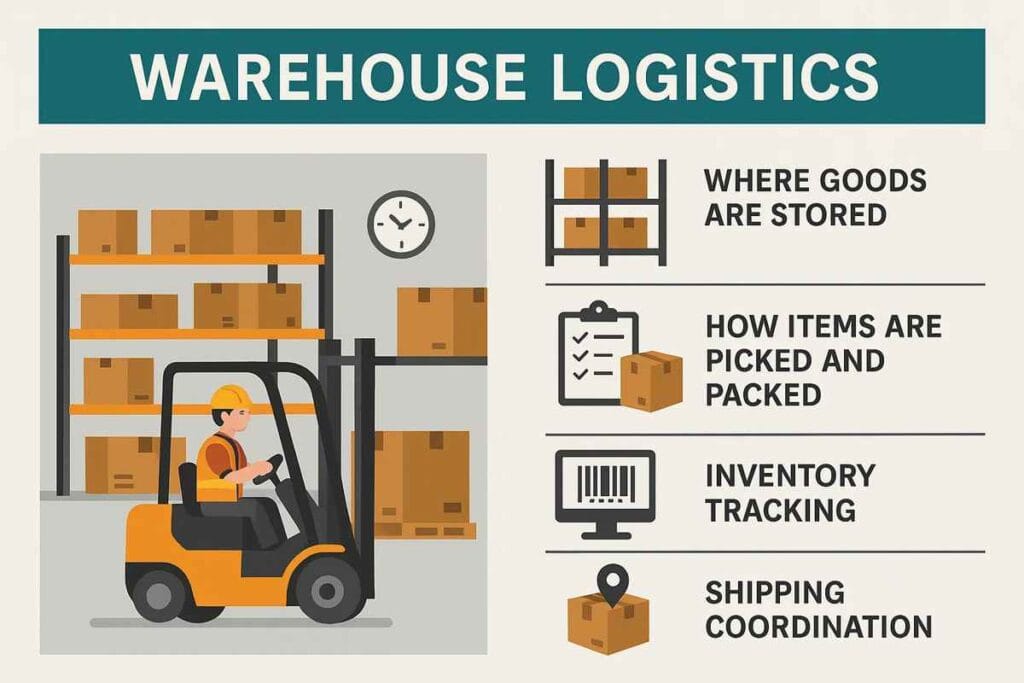
Warehouse logistics is the planning and control of everything that happens inside the warehouse. It includes:
- Where goods are stored
- How items are picked and packed
- Inventory tracking
- Shipping coordination
Good warehouse logistics means faster delivery, fewer errors, and lower costs.
What Is the Difference Between Logistics and Warehouse?
Here’s a simple breakdown:
| Logistics | Warehousing |
| Covers the full supply chain | Focuses only on storing and handling goods |
| Includes transport, inventory, delivery, and returns | Includes receiving, storing, picking, and shipping |
| Broader concept | One part of logistics |
So, logistics is the big picture. Warehousing is one crucial piece of it.
Purpose of Warehousing
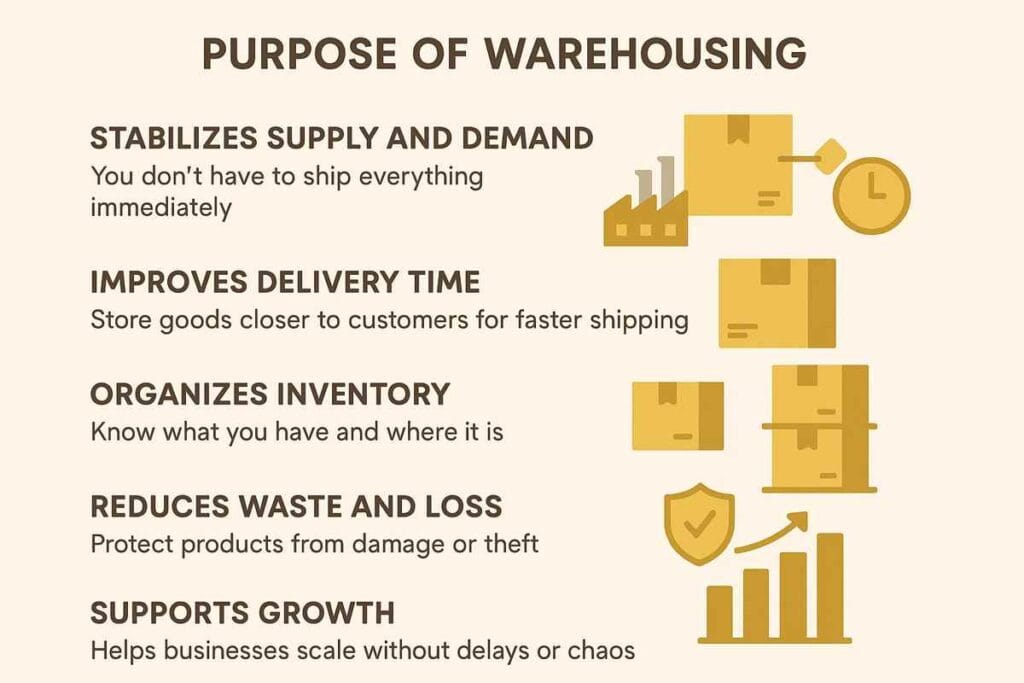
Why is warehousing so important? Let’s look at what it actually does for a business:
- Stabilizes supply and demand – You don’t have to ship everything immediately.
- Improves delivery time – Store goods closer to customers for faster shipping.
- Organizes inventory – Know what you have and where it is.
- Reduces waste and loss – Protect products from damage or theft.
- Supports growth – Helps businesses scale without delays or chaos.
Key Functions of Warehousing
Warehouses do more than hold boxes. Their main jobs include:
- Receiving – Checking and accepting incoming stock.
- Storage – Organizing items safely and efficiently.
- Inventory Management – Tracking what’s in stock, what’s low, and what’s gone.
- Order Fulfillment – Picking, packing, and shipping orders.
- Returns Handling – Managing returns without disrupting the flow.
Modern Warehousing: Going Digital
Today’s warehouses are getting smarter. Many use tools like:
- Barcodes and RFID to track goods in real time
- Warehouse management systems (WMS) to plan and optimize workflows
- Automation tools like smart conveyors or even robotic pickers
This is especially useful for e-commerce, where speed and accuracy matter.
Conclusion
So, what is a warehouse really? It’s not just a place to store products. It’s a working part of your business that helps you stay organized, ship on time, and keep customers happy.
Whether you’re using a third-party warehouse or managing your own setup, knowing how warehousing fits into your logistics can help you run things more smoothly and make smarter decisions as you grow.
FAQs
1. What is a warehouse in simple terms?
A warehouse is a building where goods are stored before being sold, used, or shipped. It helps businesses manage inventory and deliver products efficiently.
2. What is the main purpose of warehousing?
The main purpose of warehousing is to store products safely, manage inventory, and support fast, organized shipping. It also helps balance supply and demand.
3. What is the difference between a warehouse and storage?
Storage means keeping goods in a space for future use. Warehousing includes storage, plus inventory tracking, order fulfillment, and logistics processes.
4. What does third-party warehousing mean?
Third-party warehousing means outsourcing storage and logistics to a company that handles your inventory, shipping, and sometimes returns.
5. How does warehouse logistics work?
Warehouse logistics includes planning and controlling everything inside a warehouse—where goods go, how they’re moved, picked, packed, and shipped.



