Efficient warehouse management isn’t just about keeping shelves in order. It’s about cutting costs, avoiding delays, and staying ahead in a fast-moving market. Below are the most effective, human-tested, and tech-supported warehouse management best practices that will help you run a warehouse that actually works.
20 Warehouse Management Best Practices
Best practices are more than just buzzwords—they’re essential steps to keep your warehouse efficient, accurate, and profitable. Whether you’re running a small fulfillment center or a large-scale distribution operation, the following warehouse management best practices help minimize waste, streamline processes, and improve team performance.
1. Use a Warehouse Management System (WMS)
A WMS helps you track inventory, manage tasks, and automate routine operations. It connects with your ERP and reduces manual errors. According to Logistics Management, 82% of companies using a WMS report improved order accuracy.
2. Track Your KPIs
Monitor metrics like order picking accuracy, inventory turnover, and receiving efficiency. These numbers tell you what’s working and what needs fixing. For example, tracking your order cycle time can reveal delays in packing or shipping.
| KPI Name | What It Measures | Why It Matters |
| Inventory Turnover | How often stock is sold/replaced | Reduces excess inventory & costs |
| Order Accuracy Rate | Correct orders vs. total orders | Impacts customer satisfaction |
| Receiving Efficiency | Items received per hour | Optimizes inbound operations |
| Pick and Pack Cycle Time | Time from order to ready-to-ship | Speeds up fulfillment |
| Space Utilization Rate | Used vs. available warehouse space | Helps avoid overcrowding or underuse |
3. Optimize Warehouse Layout
Design aisles wide enough for forklifts and create clearly defined zones for receiving, storage, and shipping. One of the best practices for warehouse management is placing fast-moving items near packing stations to cut down on walk time and reduce order fulfillment delays.
4. Use Barcode and RFID Scanning
Manual data entry invites mistakes. Barcode scanners and RFID systems help you track products in real time. One missed scan can cause miscounts or lost items.
5. Apply ABC Inventory Analysis
Group products into A (fast-moving), B (medium), and C (slow) categories. Store A items in the most accessible spots. This reduces picking time and speeds up fulfillment.
| Category | Description | Example Products | Storage Priority |
| A | High value, fast-moving items | Smartphones, top sellers | Closest to packing zone |
| B | Medium value, moderate turnover | Mid-range electronics | Middle racks |
| C | Low value, slow-moving | Spare parts, seasonal | Back of warehouse |
6. Implement Cross-Docking
Unload goods from incoming trucks and load them directly onto outgoing ones. This reduces storage costs. Walmart uses cross-docking to keep shelves stocked with minimal warehouse space.
7. Standardize Receiving Procedures
Make sure every product that enters the warehouse is scanned, inspected, and labeled. This avoids miscounts and mix-ups later in the process.
8. Use Dynamic Slotting
Reorganize shelf space based on real-time demand. Products that sell more during peak seasons should move closer to the packing area.
9. Perform Regular Cycle Counts
Instead of a full physical inventory, do small, frequent counts. This keeps your numbers accurate without stopping operations.
10. Preplan Picking Waves
Group orders to reduce travel time. A WMS can schedule picking tasks based on product location and shipping deadlines.
11. Reduce Touch Points
The more a product is handled, the higher the chance of damage or delay. One of the essential warehouse inventory management best practices is to minimize unnecessary steps from receiving to shipping. Fewer touch points mean faster movement, fewer errors, and lower labor costs.
12. Make Popular Products Easy to Reach
Keep best-selling SKUs near packing zones. If 20% of your products make up 80% of your sales (Pareto principle), store them where pickers can reach them fast.
13. Encourage 360° Feedback
Warehouse staff often see what management doesn’t. Let them suggest workflow improvements—they might spot inefficiencies you’ve missed.
14. Prioritize Warehouse Safety
A safe warehouse is a productive one. Use proper signage, maintain equipment, and hold regular safety training. OSHA reports that slips, trips, and falls cause over 25% of all reported warehouse injuries.
15. Train Staff Properly
Even the best tech is useless if no one knows how to use it. Train workers on systems, safety, and standard procedures. Consider gamified learning to boost retention.
16. Minimize Returns and Errors
Returns eat into profits. Focus on picking accuracy, clear labeling, and correct documentation to lower return rates.
17. Use Pick-to-Light or Voice Picking Systems
These tools guide workers to the correct items, improving speed and accuracy. Some warehouses see up to 30% faster picking times.
18. Label Everything Clearly
Use large, legible labels for racks, bins, and products. It speeds up finding and storing items, especially when integrated with scanning tools. One of the warehouse management system best practices is consistent and clear labeling, which ensures faster inventory updates and reduces picking errors across your entire operation.
19. Review and Reevaluate Often
Warehouses evolve. Set a schedule to review layouts, software, and performance metrics quarterly. Adjust what’s not working.
20. Prepare for the Unexpected
Fires, floods, supply delays—anything can happen. Have an emergency plan. Backup data and stock emergency kits. Keep safety stock for critical items.
Additional Warehouse Management Tips You Shouldn’t Miss
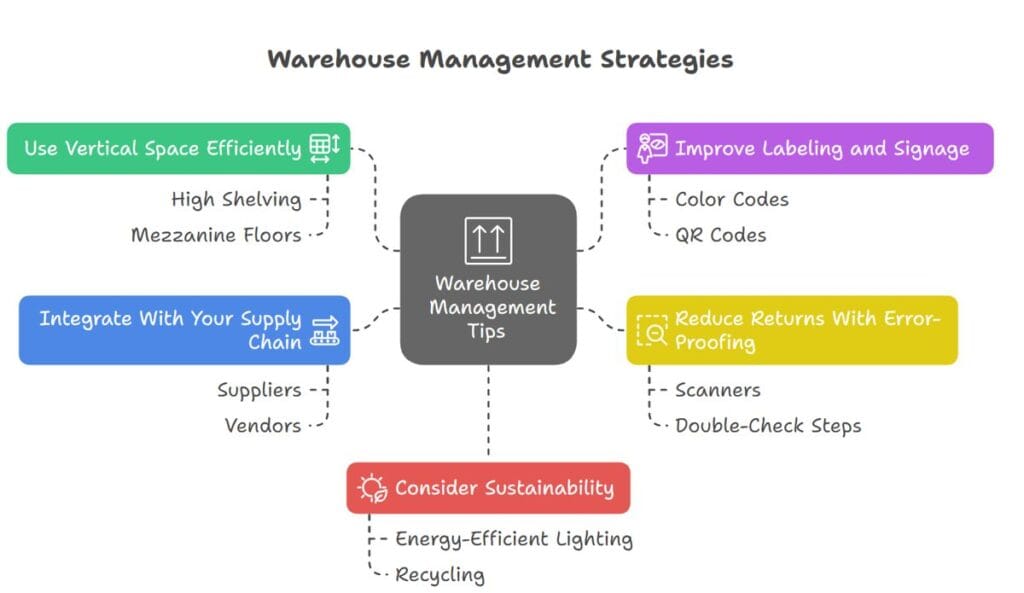
Use Vertical Space Efficiently
Instead of expanding outward, go up. Use high shelving and mezzanine floors. This can increase storage capacity by up to 40%.
Improve Labeling and Signage
Clear signs reduce confusion. Use color codes or QR codes to direct traffic and help new workers adjust faster.
Reduce Returns With Error-Proofing
Use scanners and double-check steps before shipping. Returns not only waste time but cost businesses an average of 30% of the product’s value.
Integrate With Your Supply Chain
Sync your warehouse with suppliers, vendors, and even customer systems. This ensures you’re always one step ahead when demand shifts.
Consider Sustainability
Use energy-efficient lighting, minimize packaging waste, and recycle. This not only cuts costs but attracts eco-conscious buyers.
Want help setting up your WMS or fixing what’s not working in your warehouse? Let us know—we can walk you through every step.
How to Choose the Right WMS for Your Warehouse
Not all WMS solutions are equal. Choose one that integrates with your current systems, supports real-time tracking, and is easy for your team to learn. Look for cloud-based tools if you want scalability without major infrastructure investment.
Warehouse Layout Templates That Actually Work
A warehouse layout affects efficiency. Basic templates like U-shaped, I-shaped, or L-shaped designs can be adapted depending on your space and operation type. Design with flow in mind: receiving → storage → picking → packing → shipping.
Read more: Types of Warehousing: A Simple Guide for Smarter Storage
How to Train Warehouse Staff Quickly and Effectively
Fast onboarding means less downtime. Pair new hires with experienced workers, use simple visual SOPs, and consider digital training tools with short quizzes. Gamified learning increases retention and makes the process engaging.
Final Thoughts
Warehouse management best practices aren’t about doing one thing better. They’re about doing 20 things 5% better—every day. These best practices will help you create a warehouse that runs smarter, faster, and with fewer headaches.
Start small. Pick 3 improvements from this list and implement them. Then build from there.
Your bottom line will thank you.
FAQs
1. What are warehouse management best practices?
They are proven strategies that improve how inventory is received, stored, picked, packed, and shipped. These include using a warehouse management system (WMS), tracking KPIs, organizing layouts by product demand, and minimizing manual input and touchpoints.
2. Why is a warehouse management system (WMS) important?
A WMS helps you manage inventory in real time, improve picking accuracy, speed up fulfillment, reduce paperwork, and connect with other systems like ERP or accounting tools. It simplifies complex operations and boosts overall efficiency.
3. How often should you cycle count inventory?
It depends on your business size and item value. High-value or fast-moving items should be counted monthly or weekly. Other products can be counted quarterly. Cycle counting avoids large inventory disruptions and keeps records accurate year-round.
4. What is dynamic slotting in warehouse management?
Dynamic slotting means adjusting product storage based on real-time demand. Instead of fixed locations, items are moved closer to packing stations when sales increase. It helps reduce picker travel time and boosts fulfillment speed.
5. How can I reduce errors in warehouse operations?
Use barcode or RFID scanning, automate data entry, standardize SKUs, train staff regularly, and track key performance metrics. These steps help avoid manual mistakes, improve order accuracy, and save time.





